While vitamins are just as important for health as macronutrients like fats, proteins, fiber and carbohydrates, they are required in far lesser quantities. They are necessary for a variety of regular biological processes, including cell development and reproduction, but their role in the cell’s ability to handle energy comes first.
Calcium and phosphate levels in the body are regulated with the aid of vitamin D. To maintain strong bones, teeth, and muscles, Vitamin D is an essential nutrient. It also helps to maintain your adaptive immune system, Grow and develop your muscle cells, and maintain the health of your skeletal system.
Lack of vitamin D can induce bone demineralization, bone discomfort from a disorder called osteomalacia in adults, and bone abnormalities like rickets in children. But more and more studies are showing how crucial vitamin D is for preventing a wide range of health issues.
What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D helps your body to absorb calcium and helps your bones in development and mineralization. It is also called a fat-soluble vitamin. Additionally, it has a role in a number of immunological, digestive, circulatory, and neurological system processes.
Recent studies indicate that vitamin D may help to prevent a number of diseases, including diabetes, cancer, heart disease, and depression. However, the connection between vitamin D and these disorders is yet unclear.
Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
The following have been linked to low vitamin blood levels:
- Increased risk of cardiovascular disease-related mortality
- Alzheimer’s disease in elder adults
- Child asthma is quite severe
- Cancer
According to the research, vitamin D may be useful for both the prevention and management of a variety of illnesses, such as type 1 and type 2 diabetes, hypertension, hyperglycemia, and multiple sclerosis.
How much Vitamin D is needed?
Children from the one-year-old need 8.5 to 10 micrograms of Vitamin D per day. For Adults, it is 10 micrograms per day. This includes the people who are at risk for vitamin D insufficiency as well as pregnant and nursing mothers. A microgram (µg) is a thousand times smaller than a milligram (mg).
International Units (IU) are sometimes used to indicate the quantity of vitamin D. 40 IU is included in 1 microgram of vitamin D. Thus, 400 IU or 10 micrograms of vitamin D are equivalent.
The U.S. National Academy of Medicine also advises that most people can safely consume up to 4,000 IU of vitamin D daily, while far greater doses may occasionally be required in order to temporarily elevate blood levels in some people.
Despite the rarity of toxicity, it is advised to steer clear of long-term vitamin D dosages beyond 4,000 IU without the guidance of a trained healthcare expert.
How to increase Vitamin D level
Sunlight, Food source, and Supplements are the three main methods to obtain vitamin D into your body. In this blog, What you need to know about each is listed below.
Sunlight

The finest source of vitamin D is sunlight, it is sometimes referred to as “the sunshine vitamin.” A special vitamin called vitamin D is produced in your body when sunlight is exposed to the cholesterol that is already present in your skin. A particular form of cholesterol found in your skin serves as a precursor to vitamin D. This substance transforms into vitamin D when exposed to UV-B sunlight. It suggests that adequate sun exposure is necessary to maintain healthy vitamin D levels.
However, excessive sun exposure also has a number of health hazards. This article explains how to maximize your vitamin D intake from the sun in a secure manner.
The hours between 10 am and 3 pm are ideal for getting the most vitamin D from the sun. The UVB rays are particularly strong, and it is also believed that the body produces vitamin D more quickly at this time.
As it is believed that exposure to the sun in the latter hours of the day also raises the chance of developing some forms of cancer, this period is also seen as being safer for solar exposure.
To obtain extra vitamin D, expose your arms, legs, back, and abdomen to sunlight. Remember to expose your back so that your body can manufacture the most vitamin D possible.
People with light skin tone require around 15 minutes in the sun, while those with a dark complexion may require an hour or more exposure to the sunlight.
Melanin is a pigment that determines the color of our skin. Compared to persons with lighter skin, those with darker skin have more melanin.
Your skin is shielded from too much sunshine by the protective effects of melanin. It acts as a kind of organic sunscreen barrier, absorbing UV rays and protecting skin from sunburn and skin cancer.
However, it also means that individuals with darker skin tones must spend more time in the sun in order to produce the same amount of vitamin D as those with lighter skin tones.
This increases the risk of vitamin D deficiency in those with dark skin.
Despite being a fantastic source of vitamin D, too much sun can be harmful to your skin. The following are some effects of excessive sun exposure – Skin cancer, heat stroke, aging skin, sunburns, eye injury, and eye damage.
The most natural approach to obtaining enough vitamin D is through regular sun exposure. To prevent eye damage, however, limit your exposure to the sun and cover any dark-coloured eyewear. Apply sunscreen if your job demands you to spend more time outside in the sun.
Food Source
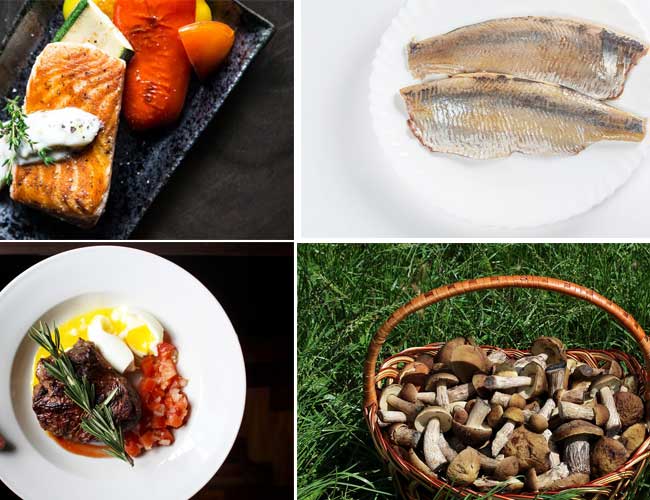

Although your body may produce some vitamin D from sunshine, you also need to get the substance through diet. The Office of Dietary Supplements (ODS) reports that there aren’t many foods that naturally contain vitamin D; the greatest sources present in fatty fishes like salmon, tuna, herring, sardines, halibut, and mackerel.
- Popular fatty seafood like salmon is a fantastic source of vitamin D. The amount of vitamin D in salmon can greatly vary depending on whether it is wild or farmed. Approximately 66 percent of the daily value (DV) for farmed salmon is present in a 3.5-ounce (100-gram) meal, whereas the DV for wild salmon can reach 160 percent.
- Each serving of tuna in a can has 269 IU of vitamin D. To stop methylmercury accumulation, choose light tuna and consume no more than one serving per week.
- Fish called herring is consumed all across the world. It is frequently pickled or smoked. This little fish also contains a lot of vitamin D.
- Sardines in cans are also a rich source of vitamin D. Per 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving of herring, there are 214 IU of vitamin D. Other healthy sources include sardines, pickled herring, and other fatty seafood like halibut and mackerel.
- A few animal foods, like cheese, fatty meats, and egg yolks, also contain trace levels of vitamin D.
- Another excellent source of really healthy food is whole eggs. The white of an egg contains the majority of the protein, whereas the yolk contains the majority of the fat, vitamins, and minerals. One large egg has 37 IU, or 5% of the DV, of vitamin D in the yolk. Since hens who have access to sunshine generate more vitamin D in their eggs than those that are kept inside, free-range and pastured eggs are excellent sources of vitamin D.
- Some types of mushrooms, which are sometimes even exposed to UV radiation to take additional vitamin D, are another excellent source. Although quantities vary depending on growing and processing conditions. Some mushroom types are morel, chanterelle, maitake, and UV-treated portabella mushrooms often contain the greatest vitamin D. The only adequate non-animal source of vitamin D is found in mushrooms. When exposed to UV radiation, mushrooms can produce vitamin D just as people can. 136 IU, or 17% of the DV, of vitamin D, may be found in one cup of these mushrooms.
- There are few natural sources of vitamin D, especially if you’re a vegetarian. Additionally, often fortified foods include cow’s milk, orange juice, cereal, yogurt, and plant-based milk (such as soy, almond, or oat milk). You may boost your vitamin D intake by eating more of these foods that are naturally high in vitamin D or that have been fortified with it.
- Natural excellent sources of numerous minerals, such as calcium, phosphorus, and riboflavin, may be found in cow’s milk. Cow’s milk has been fortified with 115 IU of vitamin D per cup (237 mL), or around 15% DV.
- Another meal that may have vitamin D added to it is cereal. 145 IU, or 18% of the DV, of vitamin D, may be found in one cup of fortified wheat bran flakes. 85 IU of vitamin D, or 11% of the DV, may be found in one cup of fortified crisp rice cereal.
Supplements

It’s not always simple to consume enough vitamin D in your diet, but it is achievable.
A supplement may be required if people aren’t eating a range of meals, particularly fish, milk, yogurt, and breakfast cereals. It’s wise to see your doctor before beginning a new supplement and to research products thoroughly before purchasing. Your doctor may prescribe a supplement or suggest an over-the-counter supplement in a dose to return your levels to normal if a blood test indicates a shortfall.
Generally, suggests a USP-verified brand with 600 IU for females up to the age of 70. This certification indicates that the product will break down and release into the body within the allotted period, contains the components indicated on the label in the claimed potency and quantities, and does not contain hazardous levels of specified contaminants.
The best approach to make sure you’re getting enough vitamin D may, for many individuals, be to take a supplement.
There are two major biological forms of vitamin D: D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol). D2 often originates from plants, whereas D3 does so from animals.
Look for a supplement with D3 rather than D2 as research shows that D3 may be much more efficient at increasing and maintaining total vitamin D levels.
The amount of vitamin D that many individuals worldwide consume is insufficient. While the sun’s UV rays can help our bodies produce vitamin D, that may not always be the most effective approach to satisfy your needs.
Nevertheless, you may increase your vitamin D levels by exposing yourself to more sunlight, consuming vitamin D-rich foods, or taking pills. The best approach to regularly and safely achieve your vitamin D needs is often through dietary sources of vitamin D or vitamin D Supplements. Some of the best sources of vitamin D are included in the list of foods in this article. Eating a lot of these vitamin D-rich foods is a wonderful approach to ensure that you receive enough of this crucial mineral.
Check your levels of this essential vitamin with a health care provider if you believe you may be deficient in it.